Shockwave Therapy for TENNIS ELBOW
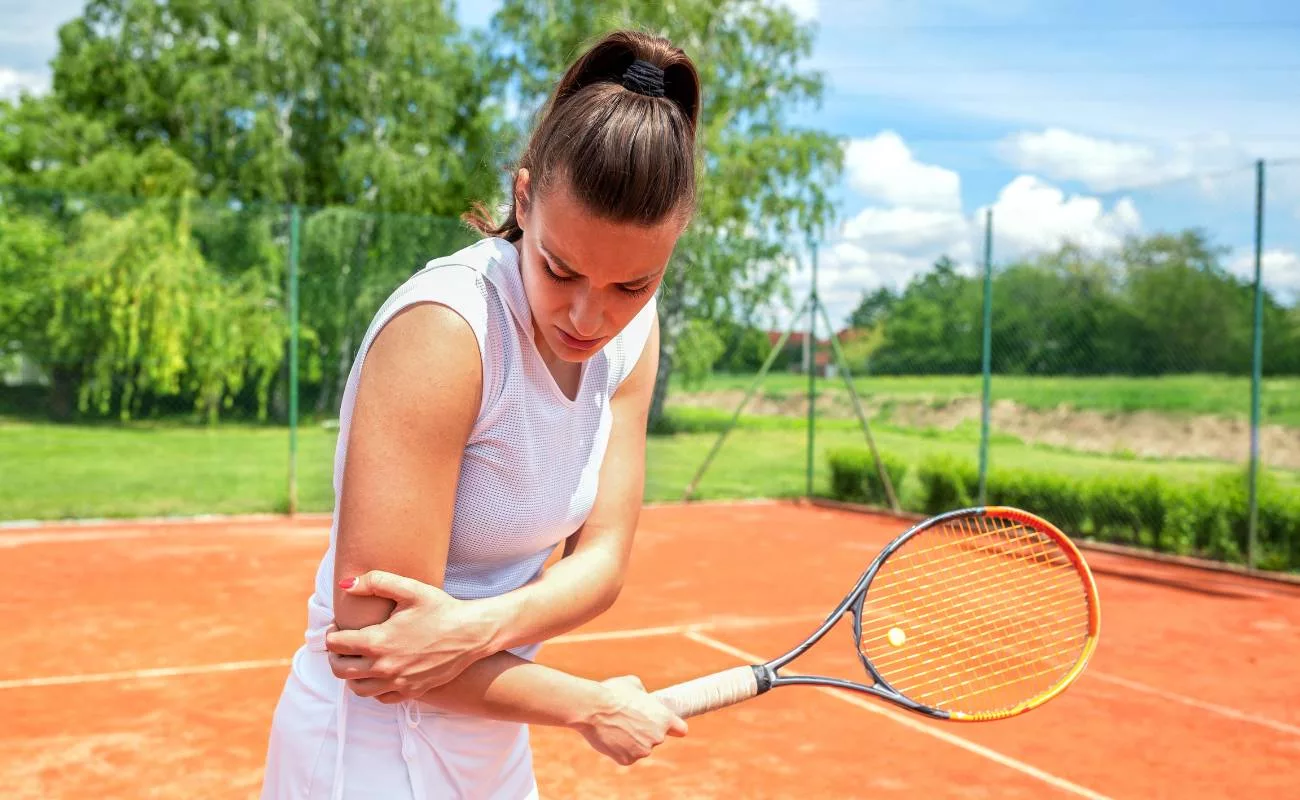
Lateral epicondylitis, commonly known as “tennis elbow,” is a painful condition involving the tendons that attach to the lateral epicondyle of the elbow. It typically results from overuse, repetitive motions, or strain on the forearm muscles and tendons. According to the Canadian Medical Association Journal, Tennis elbow has a prevalence of 1%–3%, peaking at age 35–50 years.
Shockwave therapy, also known as extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT), is a non-surgical technique used to treat various musculoskeletal conditions, including lateral epicondylitis.
1. Shockwave Promotes Neovascularization:
Shockwave therapy, a non-invasive treatment, has been recognized for its ability to promote neovascularization – the formation of new blood vessels. The mechanism behind this is multifaceted. When shockwaves are delivered to the targeted tissue, they generate microtrauma or minor injury. This controlled microtrauma triggers a series of biological responses. Firstly, there’s an immediate release of various growth factors, such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS). These growth factors play pivotal roles in blood vessel formation.
Additionally, the inflammatory response induced by the microtrauma recruits an influx of reparative cells, including macrophages. Macrophages release cytokines and other proteins that further stimulate the migration and proliferation of endothelial cells, which are the building blocks of blood vessels. Over time, these endothelial cells organize themselves to form new capillary networks, enhancing blood flow to the treated area.
Moreover, the mechanical force of the shockwave stimulates cellular mechanisms, increasing cell permeability and promoting the release of angiogenic markers. These processes collectively enhance the environment for neovascularization.
In summary, shockwave therapy’s ability to promote neovascularization arises from a combination of stimulating growth factors, instigating beneficial inflammatory responses, and directly influencing cellular behavior. This enhanced blood vessel formation plays a crucial role in healing and regeneration.
2. Shockwave Stimulates Cell Repair:
Shockwave therapy has garnered attention for its ability to foster cell repair, particularly in treating shockwaves are applied to a targeted tissue, they induce microtrauma. This intentional minor injurmusculoskeletal conditions. The therapeutic mechanism behind this involves a series of biological cascades. When y serves as a wake-up call for the body’s innate repair mechanisms.
The microtrauma from the shockwaves activates the release of various growth factors and cytokines, which are proteins that play key roles in cellular growth, migration, and differentiation. Among these is the transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), which is instrumental in tissue regeneration and repair. This factor can stimulate collagen production, a primary component of tendons and ligaments, leading to improved tissue structure.
Furthermore, the mechanical stimuli from shockwaves can increase cellular membrane permeability, allowing for the improved ingress and egress of beneficial ions and nutrients. This can enhance cellular metabolism and optimize the environment for tissue repair.
Another notable impact is on fibroblasts, cells vital for the repair of connective tissues. Shockwave therapy stimulates fibroblast activity, encouraging the synthesis of extracellular matrix components.
In essence, shockwave therapy jumpstarts the body’s natural healing processes by releasing critical growth factors, enhancing cellular functions, and activating cells pivotal for tissue repair and regeneration.
3. Shockwave Reduces Pain:
Shockwave therapy demonstrates remarkable efficacy in pain reduction. Its therapeutic action in alleviating pain can be attributed to several intertwined mechanisms. Firstly, when shockwaves are delivered to affected tissues, they create controlled microtrauma. This microtrauma disrupts the gate-control mechanism of pain transmission, temporarily inhibiting pain signals to the brain.
Additionally, the shockwaves stimulate the release of certain growth factors and induce an influx of reparative cells. This can lead to accelerated tissue repair and regeneration, indirectly addressing the root cause of pain for certain conditions.
Furthermore, shockwave therapy has been shown to reduce the production of pain mediators while increasing the release of nitric oxide, a potent vasodilator. This improved blood flow can help flush out pain-causing metabolites and inflammatory products, promoting a healing environment.
Lastly, it’s believed that shockwaves might desensitize nerve endings in the treated area, disrupting the transmission of pain impulses. This can provide both immediate and long-term pain relief for the patient.
In conclusion, shockwave therapy acts on multiple fronts to reduce pain, from direct nerve modulation and improved tissue healing to enhanced blood flow and cellular activity. This multifaceted approach makes it a valuable tool in pain management.
4. Shockwave Breaks Down Calcifications:
Shockwave therapy stands out for its capacity to address calcifications, which are hardened calcium deposits that can form within tissues and often lead to pain and restricted movement. When it comes to breaking down these calcifications, shockwave therapy operates through a set of unique mechanisms.
At the heart of the treatment is the delivery of high-energy acoustic waves to the targeted calcified areas. These waves generate forceful impacts on these hardened deposits, inducing microtrauma. This direct mechanical stress can cause fragmentation of the calcified structures, making them more amenable to the body’s natural resorption processes.
Furthermore, the microtrauma stimulated by the shockwaves activates local inflammatory responses. While inflammation is often viewed negatively, in this context, it’s beneficial. The inflammatory cells recruited to the area contribute to the phagocytosis (or “eating up”) of the fragmented calcific debris.
Additionally, the shockwaves enhance local blood circulation. Improved blood flow facilitates the delivery of reparative cells and essential nutrients to the site, aiding in the gradual dissolution and absorption of the calcified particles.
In essence, shockwave therapy combines direct mechanical disruption with the body’s natural healing and resorption processes to effectively address and break down calcifications.
Immediate Help through Physiotherapy for Tennis Elbow:
If you are suffering through conditions relating to Tennis Elbow, click below to book an appointment with one of our expert physiotherapists to let us immediately start assisting you in your road to recovery through Shockwave Therapy.
Physiotherapy Clinic Mississauga – Curezone Physiotherapy, Heartland Mississauga.
Physiotherapy Clinic Oakville – Curezone Physiotherapy, Burloak Oakville.
Read more on this topic in available in this article.